FOX EYE ANATOMY
To achieve the desired effect of "fox eyes" using the endopeel technique, it is important to have a basic understanding of facial anatomy.
To achieve the desired effect of "fox eyes" using the endopeel technique, it is important to have a basic understanding of facial anatomy.
key anatomical considerations

The shape and prominence of the orbital rim play a significant role in creating the fox eye appearance. The orbital rim refers to the bony structure around the eye socket, and its contour can be enhanced to achieve a more elongated eye shape.

The position and shape of the eyebrows can greatly influence the overall appearance of the eyes. A higher, more arched brow can help create a lifted and elongated look.

The canthal tilt refers to the angle formed by the outer corners of the eyes. A more upwardly tilted canthal angle is characteristic of the fox eye aesthetic. This can be achieved through various techniques, including the use of sutures or injectables like Endopeel.

The lateral canthal ligament holds the outer corner of the eye in place. Modifying or adjusting this ligament can help achieve the desired tilt or lift.
Frontal Muscle Elongation
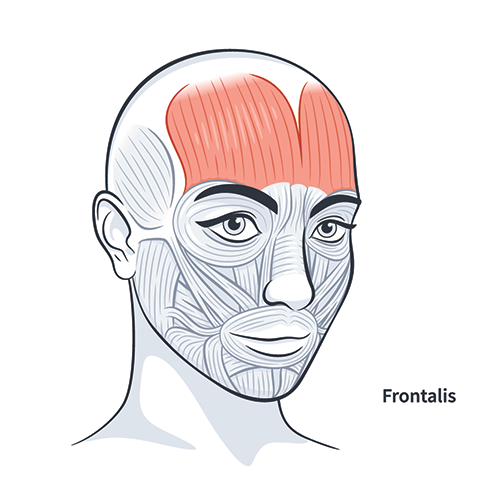

Endopeel equilibrates the muscle tone
Endopeel repositions in its anatomy any selected muscle by shortening it and projecting the muscle fibers.